Challenges like healthcare worker burnout and turnover are contributing to the estimated shortage of 10 million healthcare workers worldwide by 2030.
For 83% of healthcare leaders, improved staff satisfaction is a strategic priority for automation programmes.
And digitalisation will be key to overcoming these issues, and more, including worsening mental health and wellbeing, budgetary issues, and insufficient patient care.
Here to stay!
COVID-19 accelerated digital transformation across verticals, including healthcare.
This was critical to delivering healthcare to patients who could not leave their homes due to various lockdown restrictions, forcing patients and clinicians to become more accepting of telemedicine.
While most health executives recognise the long-term benefits of digital transformation, many struggle with how to get started while under immense resource strain
But, now that the pandemic is winding down, digital transformation has proven that it is here to stay.
While most health executives recognise the long-term benefits of digital transformation, many struggle with how to get started while under immense resource strain.
For example, while the UK and Scandinavian countries are using digitisation to help with margin pressures, the US and Australia are letting such pressures curtail the adoption of new technologies.
Making progress
So, how can digitalisation help organisations overcome resource challenges?
Around the world, patients are struggling to meet their care needs due to a system that is at overcapacity.
In the UK, for instance, the public healthcare crisis has led many patients to seek out private healthcare alternatives.
Resource strain, combined with the legacy infrastructures present in most health organisations, and tightening regulatory procedures, has made this a difficult area to make progress in.
Even when it comes to electronic health records (EHRs), an area where many countries are making strides, the issue of interoperability remains.
And this precludes the effective, timely, and secure transmission of patient data.
Resource strain, combined with the legacy infrastructures present in most health organisations, and tightening regulatory procedures, has made this a difficult area to make progress in
Intelligent automation has the potential to fill these gaps, unburdening healthcare workers so they can focus on the human side of healthcare, streamlining administrative tasks, improving patient access to care, enhancing patient engagement and experience, and enabling collaboration between healthcare professionals and organisations.
Intelligent automation consists of different advanced technologies, including robotic process automation (RPA), artificial intelligence (AI), and business process management (BPM), working complementarily as digital workers to drive outcomes:
Intelligent automation consists of advanced technologies including robotic process automation and artifical intelligence
Robotic process automation
RPA can automate routine administrative tasks, such as appointment scheduling, claims processing, and data entry. This frees up healthcare professionals to focus on complex, higher-value tasks, like patient care and research.
RPA also minimises errors and improves efficiencies by replacing manual processes that are completed by overworked and overtired health workers.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning (ML)
AI and ML can analyse large amounts of healthcare data to uncover patterns and insights that can inform decision-making.
For example, ML algorithms can help identify patients who are at high risk for certain conditions, allowing healthcare providers to intervene earlier and potentially prevent more-serious health issues, as well as save costs and time down the line.
These technologies can also be used to develop predictive models for hospital readmissions, disease progression, and patient outcomes, allowing providers to deliver more-personalised care and improve outcomes.
Business Process Management
BPM can help healthcare organisations streamline and co-ordinate their processes, reducing the time and resources required to perform routine tasks.
BPM can also help healthcare organisations identify and eliminate bottlenecks in their processes, allowing them to operate more efficiently and effectively long term.
Making the transformation
The patient treatment flexibility intelligent automation can deliver saves costs and time.
For example, treating patients in lower-acuity settings, like their home, is less costly.
And using digital workers to confirm patient appointments, address routine queries, and aggregate all patient information has a substantial impact on health professionals’ workloads, as well as organisational efficiency and costs.
But how do health organisations optimise their digital transformation journey?
While this may seem daunting to put together, when taken step by step, and with the advice of experts, it becomes achievable
Building a business case helps clearly define your vision and its benefits. And this helps prove to key stakeholders that digital transformation is a worthwhile investment.
It should begin with a basic introduction, describing the proposed vision and accompanying benefits. From here, key questions should be addressed: What happens if you do nothing? What are the different possible procurement pathways? Are there multiple deployment options?
Next, convey what defines success, and how it will be achieved.
Lastly, longer-term plans should be proposed.
How will the proposed solution be procured?
Make sure to consider regulations and policies and information on license costs, projected revenue savings, and proposed returns on investments should be modelled.
While the above may seem daunting to put together, when taken step by step, and with the advice of experts, it becomes achievable.
Key steps to launching a successful healthcare automation programme include:
Step 1: Identify opportunities for automation
This is one of the most-important steps.
Organisations seem to be best off when they begin with simple-yet-high-volume tasks involving multiple people.
By starting with easier wins, you’re able to more easily get people on board through quantifiable proof points of the benefits of digitalisation.
Cultural adoption is crucial to success, so it’s important to get people involved in goal and roadmap structuring early on. This helps foster an automation-first culture.
By starting with easier wins, you’re able to more easily get people on board through quantifiable proof points of the benefits of digitalisation
Once you’ve identified the opportunities you want to automate, study these processes and consider limitations and workarounds.
Understanding processes before automating them is essential.
Process intelligence can be especially helpful here since healthcare organisations tend to operate across multiple systems that sit within interoperable siloes.
Process mining software can process system-level data to uncover the best tasks to automate, factoring insights and hidden steps that manual assessment can miss.
This helps organisations better overcome the inherent limitations of any existing systems.
The benefits of automation ranked as top three by health professionals around the world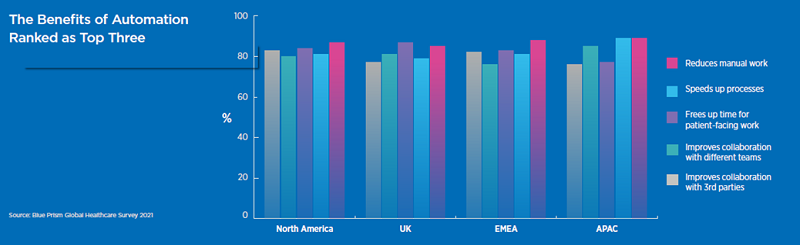
Step 2: Successfully deploying your process automations
For this step to be successful, executive sponsorship is important because it imparts a business-wide lens to the vision and offers the support and credibility needed to onboard the entire organisation.
This is key because automation success will collapse without the support of entire teams.
Team members should know their roles and responsibilities and they should have a clear understanding of how digital workers will impact them, including direct benefits.
Your developers, engineers, and consultants play an instrumental role in developing and deploying your automation infrastructure and it can be helpful to establish a centre of excellence to oversee the digital transformation journey, ensuring that actions align with overall strategic objectives and are within regulatory and governance frameworks.
Step 3: Maintenance and scaling
At this point, you should have an onboard work environment and the systems needed for success in place.
The penultimate step is the establishment of an ongoing operating model, which should include several factors: a long-term strategy that includes scaling plans, clear roles, needed skills – using education and training to fill any gaps, governance measures, and best practices.
The ongoing journey
Once you have deployed your automations, digital transformation is not complete – it’s an ongoing journey that requires a robust and agile infrastructure, combined with a culture of automation, and leaders to manage the change.
